Toolkit Downloads
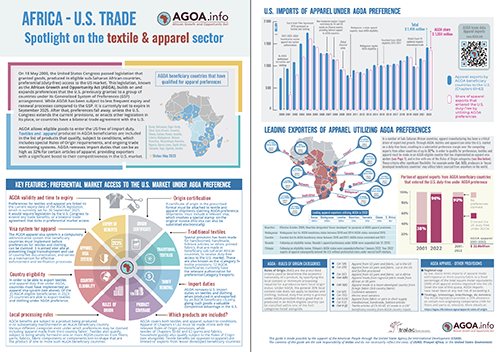
AGOA sector focus - Spotlight on textiles and trade under AGOA [Updated 2023]
An overview of key features of exports of textiles and apparel products to the US by AGOA beneficiaries, including the relevant rules of origin provisions. Double-sided A4 brochure. For optimised printing, set 'fit to page'. Includes trade data to end 2022
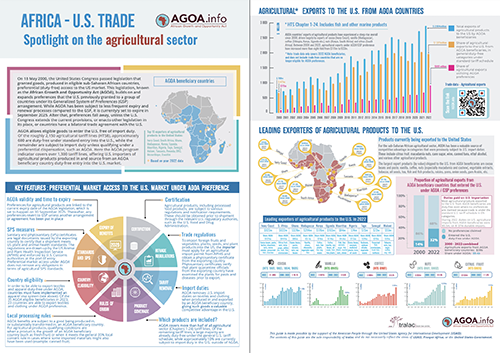
AGOA sector focus - Spotlight on agriculture and trade under AGOA [Updated 2023]
An overview of key features of the export of agricultural products to the US by AGOA beneficiary countries, including cocoa, vanilla, coffee, nuts and citrus fruit. Double-sided A4 brochure. For optimised printing, set 'fit to page'. Includes trade data to end 2022
EAC Common market implementation impact of container cash deposit requirement in Kenya: The Case of private sector firms in Rwanda
To highlight the impact of Mombasa Port container cash charges on regional trade and business, the Hub created the following case study focused on Rwanda private sector firms. The study demonstrates the need for a solution to the cash deposit requirement in order to reduce the cost of doing business. The study reveals long administrative time gaps between claim submission and deposit recovery that impact on business cash flow and adds financial burdens, particularly to smaller freight forwarders. It also leads to an increase in operational costs that are ultimately passed on to consumers. The study further reveals how the utilization of a guarantee scheme has enabled some of the firms to reduce costs.
AGOA 101 Kenya - Exporter Guide 2018
The USAID East Africa Trade and Investment Hub helps East African businesses take advantage of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). AGOA allows for duty-free export of over 6,000 products. This guide outlines the step-by-step process that Kenyan businesses should take to export to the United States of America (U.S.A.) duty-free through AGOA and gives a general overview for the export of all AGOA products from Kenya. It provides additional information on the export of four high-demand, high-value sectors, namely textiles and apparel; coffee; nuts and oil crops; and cut flowers. Although exporting can be a challenging process, it can also be profitable for the individual or company that successfully complies with the steps. Exporters must follow two sets of requirements: Kenyan laws and regulations that govern the export process, and Laws and regulations that govern the destination country’s imports, in this case, the U.S.A. Regulations also vary according to the product being exported; exporters must research to ensure that their product meets the necessary requirements for export. This guide assumes that the exporter or potential exporter has already conducted the necessary market research, and is ready to export. Before proceeding, exporters must identify the correct tariff code and its eligibility for dutyfree export under AGOA. This status can be established by referring to...
Overview of US textile requirements
The slides in this presentation are intended to be used in a training event with verbal elaboration by a knowledgeable presenter. The slides highlight key U.S. product safety requirements for this discussion. The text is not a comprehensive statement of legal requirements or policy and should not be relied upon for that purpose. You should consult official versions of U.S. statutes and regulations, as well as published CPSC guidance when making decisions that could affect the safety and compliance of products entering U.S. commerce. Note that references are provided at the end of the presentation and a handout on phthalates prohibitions in children’s toys and child-care articles is also available.
Overview of the Cotton, Textile and Apparel Sectors in East Africa Region and Benchmarking with Sri Lanka and Bangladesh
Overview of the Cotton, Textile and Apparel Sectors in East Africa Region and Benchmarking with Sri Lanka and Bangladesh is a USAID Hub report that serves as a reference for businesses looking to source from East Africa. It provides easily searchable and mapped information on sector players that could be used to identify textile, apparel and apparel accessory producers who can supply products to local and regional clients and U.S. buyers. It also benchmarks the business climate for apparel-related trade and investment in six East African countries (Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Madagascar, Mauritius and Ethiopia) against two global apparel producing competitors in Asia – Sri Lanka and Bangladesh – to provide a basis for the selection of suitable sourcing and investment for local and global buyers as well as policy improvements and interventions by East African governments.
US end-market analysis for Kenyan textiles and apparel
The apparel market in the United States (U.S.) is the largest in the world with a market value of $343 billion. In 2016, the U.S. imported apparel worth $105 billion, up from $88 billion in 2015 and $82 billion in 2014.1 U.S. consumers spent $312 billion on apparel. Ten countries account for almost 80 percent of all U.S. apparel imports with China topping the list with a 30 percent share. While Kenya does not yet stand among these countries, there is an opportunity for Kenya to take advantage of its trade preferences under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) to increase its exports to the U.S. market. Since AGOA was signed for an additional ten-year term in 2015, there has been a growing trend toward sourcing and importing apparel to the U.S. If more stakeholders in both countries realize AGOA’s full potential, Kenyan apparel exports can continue to climb. This report focuses on six target product opportunities for Kenyan exporters: Knitted Shirts in Synthetics for all genders and ages T-shirts in Cotton and Synthetic for all genders and ages Sweaters in Synthetic for all genders and ages Woven Pants and Shorts in Cotton and Synthetic for all genders and ages Woven Shirts in Cotton and Synthetic for all genders and ages Dresses for Women and Girls in Cotton and Synthetic as part of SME products These products were determined by volumes and trends and are not unique to Kenyan production. However, these products offer opportunities for large duty...
US end-market analysis for Kenyan cut flowers
Cut flowers are a major export industry in Kenya. Kenya presently ranks first among world exporters of roses to the European Union (EU), with a market share of 38 percent. However, the country has not yet made as deep of inroads into the cut flower market in the United States (U.S.). Kenyan cut flower exports to the U.S. have grown since 2010, but the country’s market share remains small, standing at 1 percent. This report analyzes emerging opportunities to increase Kenyan flower exports to the U.S. while taking advantage of the benefits granted under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). In 2016, Kenya ranked as the twelfth greatest supplier of cut flowers to the U.S. Nearly 90 percent of the cut flowers imported by the U.S. come from three countries: Colombia (59 percent), Ecuador (22 percent) and the Netherlands (7 percent). Colombia and Ecuador, who make up more than 80 percent of the imported flowers, present stiff competition. The countries profit from longstanding commercial relationships with the U.S. and geographic proximity, which reduces freight and transport costs. Both countries enjoy duty-free access to the U.S. market, as does Kenya. Nonetheless, Kenya has a strong, competitive cut flower industry that is ready to explore new markets. The industry is profitable and technically competent, it has developed efficient logistics to the European markets and it offers high-quality flowers at competitive prices. If the industry can use these strengths...
US end-market analysis for Kenyan home decor and fashion accessories
This report provides market data at a product level for use by Kenyan exporters interested in the United States (U.S.) market and to support the National African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) Strategy and Action Plan for Kenya. The home décor and fashion accessories sector has the capacity to further the goals of increasing women and youth participation in manufacturing by providing greater access to economic opportunities. In 2016, the top preforming Kenyan product categories in this sector represented $5.2 million in exports to the U.S. The U.S. is the largest importer in the world in all categories, and the fourth largest in jewelry. This report analyzes the top supply growth opportunities for Kenya based on the U.S. import demand. It also presents the current market trends in the U.S. for Kenya to better compete internationally. In addition, the Kenya Vision 2030 makes the recommendation for "a better and more inclusive wholesale and retail trade sector." Accomplishing the goal of increasing efficiency, lowering transaction costs and strengthening trade as well as linking trade to wider local and global markets requires: Understanding the demands of the international market and the trends that influence the global exports to the U.S. market; Understanding the advantages of the Kenyan market in key product categories, competitiveness in raw material sourcing, and the international competitors participating on the global stage; Sharing a detailed explanation...
US end-market analysis for Kenyan tea
The tea market in the United States (U.S.) is growing, with Americans consuming larger quantities of tea each year. In 2016, the U.S. imported nearly $760 million in tea (excluding herbal tea), making it the world’s third largest tea importer.1 According to the Tea Association of the USA, the sector projects compound annual growth rates of 3 to 5 percent over the coming years. This has been driven by an increase in volume, but especially value, of tea imports. Approximately four out of five Americans drink tea. For Millennials, tea consumption reaches an estimated 87 percent. This population, in particular, is driving the upward trend in tea consumption and price. Consumers are becoming more health-conscious and are therefore willing to pay for better quality tea and innovations in flavors, packaging, and convenience. Black tea, specialty teas, and Ready-to-Drink (RTD) tea are experiencing the highest rates of growth. Black tea, which accounts for 85 percent of U.S. tea consumption, achieved 2.3 percent growth in imports between 2015 and 2016. Sales of specialty teas, comprised of loose-leaf teas, single-estate teas, Fairtrade, organic, or rare teas, are increasing about 10 percent per year. Further, RTD tea is expected to grow 4 to 6 percent over the next five years. The U.S. market is highly competitive. It is comprised of a handful of U.S. growers and numerous importers that are supplied by exporters from almost every tea producing country. In 2016, the U.S....
US end-market analysis for Kenyan speciality coffee
The United States of America (U.S.) is the largest market for coffee in the world. Within the U.S. coffee sector, the specialty coffee industry imports almost 750 million kilograms (kg) of green, specialty-grade coffee from around the world each year, often paying double the commodity price. Specialty-grade coffees are identified by their high-quality, unique taste characteristics and countries of origin. They are roasted by one of 1,400 U.S. roasters and distributed to hundreds of thousands of coffeehouses, supermarkets, restaurants, and specialty stores. Whether prepared by retailers or sold in bulk packages for self-preparation at home or in the workplace, 35 million Americans drink specialty-grade traditional coffee on a daily basis. As geographic origin plays a major role in the taste and body characteristics of specialty coffee, it can be broadly distinguished by growing region – Latin America, Asia/Pacific or Africa. East Africa currently contributes about 4 percent to the volume of annual U.S. green Arabica imports, the predominant species of specialty-grade coffee. Imports from Kenya alone account for about 6 percent. While Kenya could improve issues related to the price and volume of quality production, the country has historically had a reputation for quality and continues to compare favorably with other countries. In fact, Kenyan AA1 was the first single-origin coffee widely identified by its origin name in the early days of the U.S. specialty coffee...