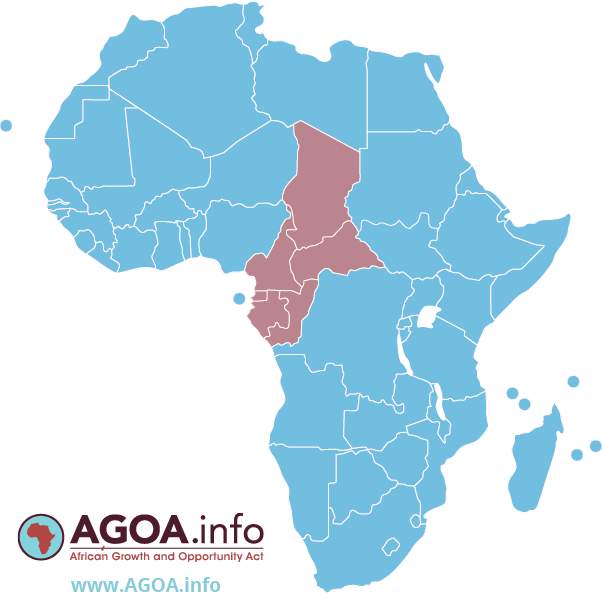
Regional Info: CEMAC
Bilateral Trade by Sector: United States - CEMAC
Value ('1000 dollars), US 'domestic exports' *, US 'imports for consumption' / Includes year-to-date data Data covers AGOA beneficiaries only
Economic Background
The Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) (French: Communauté Économique des États de l'Afrique Centrale) includes six countries: Cameroon, Congo (Brazzaville), Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, the Central African Republic and Chad. Its stated mission is to promote the harmonious development of Member States in the framework of the establishment of a true common market.
Currently, CEMAC countries share a common financial, regulatory, and legal structure, and maintain a common external tariff (CET) on imports from non-CEMAC countries.
In theory, tariffs have been eliminated on trade within CEMAC, but full implementation of this has been delayed meaning that the objectives of a full customs union have not yet been met.
The treaty which established CEMAC in its current state was signed on March 16, 1994, in N'djamena (Chad). It replaced the treaty establishing the Customs and Economic Union of Central Africa (UDEAC), signed on December 8, 1964, in Brazzaville. (Sources: CEMAC Secretariat and Wikipedia)
Of the CEMAC member states, only Cameroon, Congo (Brazzaville), Gabon and Chad are AGOA beneficiaries. Their trade data is included in the US-CEMAC trade table alongside.