Country Info: Gabon
Bilateral Trade by Sector: United States - Gabon
Value ('1000 dollars), US 'domestic exports' *, US 'imports for consumption' / Includes year-to-date data
Economic Background
[Gabon has had its AGOA preferences suspended effective 1 January 2024]
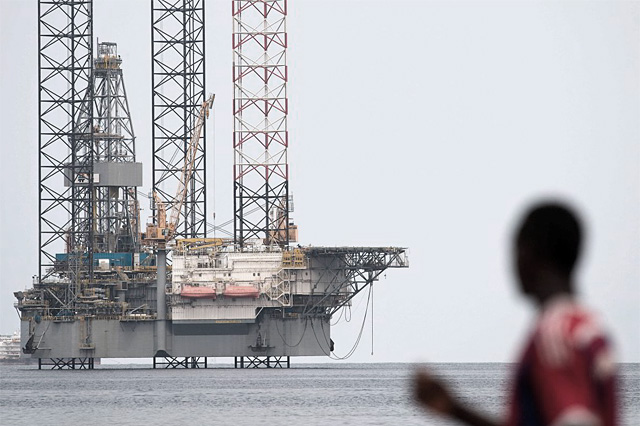
Gabon enjoys a per capita income four times that of most Sub-Saharan African nations, but because of high income inequality, a large proportion of the population remains poor. Gabon relied on timber and manganese exports until oil was discovered offshore in the early 1970s.
From 2010 to 2016, oil accounted for approximately 80% of Gabon’s exports, 45% of its GDP, and 60% of its state budget revenues.
Gabon faces fluctuating international prices for its oil, timber, and manganese exports. A rebound of oil prices from 2001 to 2013 helped growth, but declining production, as some fields passed their peak production, has hampered Gabon from fully realizing potential gains. GDP grew nearly 6% per year over the 2010-14 period, but slowed significantly from 2014 to just 1% in 2017 as oil prices declined.
Low oil prices also weakened government revenue and negatively affected the trade and current account balances. In the wake of lower revenue, Gabon signed a 3-year agreement with the IMF in June 2017.
Despite an abundance of natural wealth, poor fiscal management and over-reliance on oil has stifled the economy.
Power cuts and water shortages are frequent. Gabon is reliant on imports and the government heavily subsidizes commodities, including food, but will be hard pressed to tamp down public frustration with unemployment and corruption.
Agricultural products
plantains, cassava, sugar cane, yams, taro, vegetables, maize, groundnuts, game meat, rubber
Industries
petroleum extraction and refining; manganese, gold; chemicals, ship repair, food and beverages, textiles, lumbering and plywood, cement
Industrial production growth rate
1.8% (2017 est.)
(Source: World Factbook, 2013)