Toolkit Downloads
US end-market analysis for Kenyan speciality coffee
The United States of America (U.S.) is the largest market for coffee in the world. Within the U.S. coffee sector, the specialty coffee industry imports almost 750 million kilograms (kg) of green, specialty-grade coffee from around the world each year, often paying double the commodity price. Specialty-grade coffees are identified by their high-quality, unique taste characteristics and countries of origin. They are roasted by one of 1,400 U.S. roasters and distributed to hundreds of thousands of coffeehouses, supermarkets, restaurants, and specialty stores. Whether prepared by retailers or sold in bulk packages for self-preparation at home or in the workplace, 35 million Americans drink specialty-grade traditional coffee on a daily basis. As geographic origin plays a major role in the taste and body characteristics of specialty coffee, it can be broadly distinguished by growing region – Latin America, Asia/Pacific or Africa. East Africa currently contributes about 4 percent to the volume of annual U.S. green Arabica imports, the predominant species of specialty-grade coffee. Imports from Kenya alone account for about 6 percent. While Kenya could improve issues related to the price and volume of quality production, the country has historically had a reputation for quality and continues to compare favorably with other countries. In fact, Kenyan AA1 was the first single-origin coffee widely identified by its origin name in the early days of the U.S. specialty coffee...
Presentation on business planning instruction and business plan template
Executive Summary Brief history and ownership structure of the business Markets and competition Marketing and selling methods Products Manufacturing processes Historical Trading or export performance Management and personnel Financial analysis and underlying performance Risks and Rewards
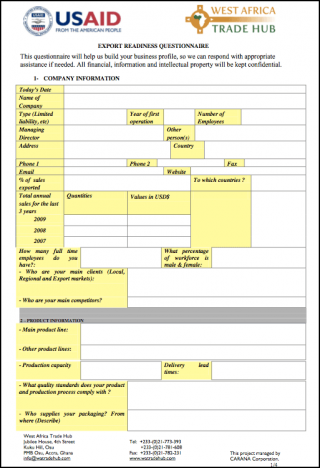
Export readiness assessment
The following "Export Readiness Assessment" is a set of questions designed to assess how prepared your company is to begin exporting to the U.S. The test is designed to identify weak areas in your company's planning so they can be redressed before commencing with the implementation of an export strategy.
Packaging in West Africa - A resource guide (Tradehub) - ANNEX
The purpose of this directory (Annex to West Africa Packaging Guide) is to help food industry producers identify manufacturers in their country or subregion capable of offering the packaging they need. Its agenda has a sales/marketing goal as opposed to a technical one. This ANNEX 1 contains country information sheets with types of materials listed. We have focused on the most widely used packaging materials, namely plastic and cardboard. The information sheets are structured as follows: Section 1: Type of material Section 2: Company address Section 3: Options offered by the company for the material concerned Section 4: Basic information for commercial
Packaging in West Africa - A resource guide (Tradehub)
Most small and medium-sized African businesses have difficulty sourcing affordable quality packaging for their products. Few packaging suppliers exist within the region and even fewer have the ability to create packaging that meets international standards and satisfies consumer preferences. Many African producers therefore turn to Europe and North America for packaging supplies, which significantly increases operating costs. In spite of the lack of quality packaging supplies in West Africa compared to Europe and North America, some sources do exist within the region; it is simply a matter of identifying them. It is in this context that the West Africa Trade Hub developed this resource guide for packaging in West Africa. The guide’s main objective is to offer practical suggestions on packaging and help food industry operators access information about packaging that will support the growth of their businesses. A case study is included that applies these suggestions and demonstrates the utility of this guide. The guide begins with an overview of the demand for packaging in West Africa and reviews different types of packaging, examining their relative advantages and disadvantages. The guide highlights the importance of good packaging, which can significantly influence sales of the finished product. High quality packaging is defined not only by its visual appearance, but also by the choice of words and graphics on labels as well as its compliance with local and...
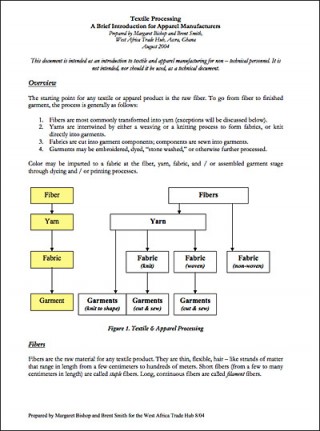
Raw materials traceability for US apparel imports - 2005
Raw materials traceability is the ability to identify, through a comprehensive system of lot numbers and documentation, the source of each and every fabric and trim used to produce a given garment.
APHIS Commodity import approval process for agricultural products into the US
To obtain access to U.S. markets for a fruit, vegetable, plant, or plant product that is not already an approved commodity, one must initiate a commodity import request. There are 4 steps in the process: Determine if the commodity is an approved commodity or currently undergoing a pest risk analysis If it is not approved or currently undergoing a pest risk analysis, submit a commodity import request APHIS will conduct a pest risk analysis and an environmental review to determine potential pests likely to remain on the commodity upon importation and potential mitigations that may be required to avoid, reduce, or eliminate the risk of pest introduction. If APHIS determines that the commodity can be safely imported into the United States, APHIS will initiate the regulatory administrative process to seek public comment
APHIS Permitted fruit and vegetables into the US - APHIS Guide 2012
The Fruits and Vegetables Import Manual provides the import requirements for regulating imported articles of fresh, usable parts of plants such as fruits, stems, leaves, roots, and flowers (herbs and vegetables). These imported articles are not intended for planting or growing, but they might serve to introduce exotic pests.
Questions and Answers: Importing irradiated fruit into the United States
Factsheet produced in 2008 by the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, United States Department of Agriculture, on importing irradiated fruit into the United States
Category 9 Determinations on eligibility for textile exports under AGOA - all countries
Schedule of determinations, for each applicable AGOA beneficiary, relating to Category 9 articles under AGOA: Traditional and folklore textiles
Category 9 Textiles - US Customs and Border Protection slides on applicable preferences - 2003
US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) slides on Folklore and Category 9 benefits
GSP Handbook (UNCTAD) 2003
Handbook / Guide on the General System of Preferences (GSP) of the United States. This guide includes features of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) as it relates to the GSP. Prepared by the UNCTAD Technical Cooperation Project on Market Access, Trade Laws and Preferences.
Category 9 Textiles - Guide for eligible governments to the application for traditional fabrics to be included under AGOA
Instructions for beneficiary country governments to apply for approval of handloomed / handmade / folklore articles under Category 9
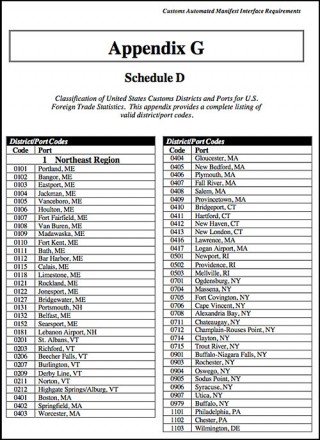
Lists and codes of US ports (a customs requirement)
Classification of United States customs districts and ports for US foreign trade. This appendix provides a complete listing of valid district/port codes of the U.S., and is important information for exporters and shipping agencies.
Review of AGOA certificate of origin - request for comments 2013
U.S. Customs and Border Protection is extending through August 14, 2013 the period for public comment on the proposed extension of the African Growth and Opportunity Act Certificate of Origin. For preferential treatment under AGOA, the exporter is required to prepare a certificate of origin and provide it to the importer. This certificate includes information such as contact information for the importer, exporter and producer; the basis for which preferential treatment is claimed; and a description of the imported merchandise. Importers are required to have the certificate in their possession at the time of the claim and to provide it to CBP upon request.
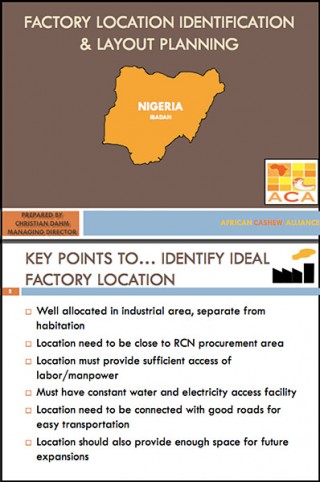
AGOA Countries: Challenges and considerations in exporting horticultural products to the United States
Congress, the Administration, and other stakeholders continue to be involved in serious efforts to improve upon the African Growth Opportunity Act (AGOA), which was first signed into law a decade ago, on May 18, 2000. To meet its objective of enhancing U.S. market access for subSaharan African countries that are pursuing market reforms measures, the AGOA preferential trade legislation was designed to encourage and support countries in this region ―that are taking often difficult but critical steps necessary to create more open, market and growth-oriented economies.‖1 AGOA eligibility currently extends to 38 African countries, with some benefitting from exports of natural resources such as oil and minerals, while others have been able to develop textile and apparel industries in which goods are more easily manufactured and exported without barriers to market in the United States. Nigeria and Angola are leading oil producers and suppliers to the U.S.; these two countries alone accounted for 80 percent of all AGOA imports in 2008. In contrast, the value of agricultural exports to the United States from 14 other AGOA-eligible countries was less than $1 million in 2009. In fact, three of these countries – Namibia, Seychelles, and Chad had less than $100,000 in agricultural exports under AGOA in 2009 (see Annex A).
Ethiopia coffee industry value chain analysis (USAID / COMPETE 2010)
Profiling the actors, their interactions, costs, constraints and opportunities. The birthplace of coffee, Ethiopia is home to some of the finest coffees in the world. Ethiopia is currently the top African coffee exporter and ranked sixth in the global market. Ethiopia exported 170,888 tons of coffee and earned $525.2 million during June/July 2007/08 period compared with 176,390 tons worth $424.2 million in 2006/07. Coffee generates 70 percent of Ethiopia‘s foreign exchange earnings and provides livelihoods for 15 million Ethiopian smallholder farmers. The coffee economy employs several hundred thousand workers in processing either red cherry (key eshet) or dried pulp coffee (jenfel) in hundreds of washing stations and hulling mills around the country. Government institutions are responsible for the state coffee plantations with approximately 8000 permanent employees and an estimated 50,000 casual jobs annually. Coffee generates a considerable number of jobs on-farm, in the processing plants and in the transport sector. In Ethiopia, coffee constitutes a very important source of casual employment for many poor people and most agro-processing employees are women.
Burundi coffee supply value chain analysis (USAID / COMPETE 2010)
Profiling the actors, their interaction, costs constraints and opportunities. The coffee industry is the country's main export, providing about 70% of foreign currency revenues. Roughly 600,000 rural households, or almost 40% of the population, grow coffee and coffee represents an important source of income in the family economy. The Burundian farmer’s interest in growing coffee is based on the fact that coffee is a seasonal product that provides a chunk of income larger than what the farmer is able to save during the course of the year. According to the latest statistics available, income from coffee growing provides 50% of family income in the northern region of Buyenzi1. This revenue allows the farmer to finance house construction and send children to school, as well as other small investments. In addition, with the initiation of micro-credit schemes in rural areas, ownership of coffee trees is the main guarantee that farmers can offer micro-credit institutions (COOPEC2 and others). It worth noting that the construction of de-pulping stations in rural areas led to the (modest) beginnings of industrialization, employment for local labor during the coffee campaign and the opening up of rural areas through the construction of factory access roads which are also used for other purposes.