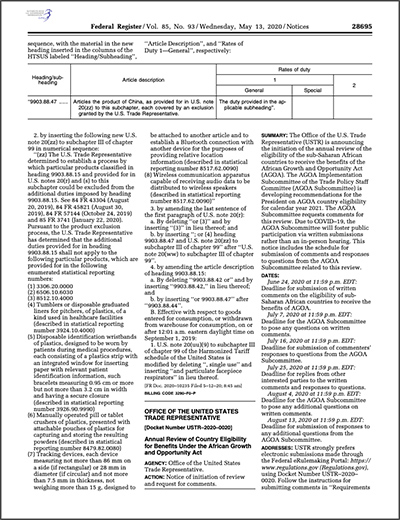
AGOA Country Eligibility
LIST OF AGOA BENEFICIARIES
List of AGOA-eligible countries, date of eligibility, and status of compliance with AGOA's 'Wearing Apparel' and Category 9 "traditional and folklore fabric" provisions.
Background
AGOA eligibility requirements are set out in Section 104 of the AGOA legislation (Public Law 106/200). Only Sub-Saharan African countries are considered for eligibility, and with AGOA beneficiary status having been awarded to approximately 40 countries (this number changes from time to time).
While the eligibility requirements are set out in the legislation, it is the United States which determines, annually, whether countries have met the published eligibility requirements. Beneficiary status may therefore be granted, or withdrawn, at the discretion of the US President.
Beneficiary countries have no recourse to dispute settlement in this regard, and this unpredictability is one aspect that differentiates AGOA’s non-reciprocal preferences to those contained in reciprocal and bilateral trade agreements.
On October 2, 2000, former US President Bill Clinton designated 34 Sub-Saharan African countries as eligible for the trade benefits provided under AGOA.
On January 18, 2001, Swaziland (Eswatini) was designated as the 35th AGOA eligible country and on May 16, 2002 the Ivory Coast (Côte d'Ivoire) was designated as the 36th AGOA eligible country (the Ivory Coast subsequently lost, and later regained beneficiary status).
The Gambia was declared eligible on January 1, 2003, while the inclusion of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) was subsequently backdated to January 1, 2003 (the DRC has since lost its status).
On 31 December 2003, the Central African Republic (CAR) and Eritrea were removed as AGOA-beneficiaries (Central African Republic was reinstated on 15 December 2016), followed later by Mali and Madagascar, while Angola was included. Other additions to this list are Burkina Faso and Burundi, while Mauritania has been suspended. In December 2006, the Republic of Liberia was also added. Countries not eligible for AGOA are Zimbabwe and Sudan, although South Sudan had since been granted beneficiary status, but has lost it again from 2015 onwards, as did The Gambia. Guinea Bissau regained eligibility, as did Madagascar earlier in 2014.
Eswatini (formerly known as Swaziland) has also been suspended from AGOA preferences, applicable from 2015, but has since been reinstated as of December 2017.
On 30 September 2015, Seychelles was graduated out of AGOA effective 1 January 2017 due to the country gaining developed country status . During 2018, the AGOA preferences for Mauritania were suspended (effective 2019) while Rwanda had its AGOA preferences suspended for the apparel sector.
On 15 December 2016, the Central African Republic regained AGOA eligibility status.
On 26 December 2019, Cameroon lost it AGOA eligibility status, effective 1 January 2020.
On 22 December 2020, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) was reinstated as an AGOA beneficiary country, effective 1 January 2021. At the same time, the DRC was also declared an eligible 'lesser developed beneficiary sub-Saharan African country' for purposes of textile preferences under the favourable third country fabric rules of origin. At this time it had however not yet met the apparel visa requirements.
On 23 December 2021, Ethiopia, Guinea and Mali had their AGOA beneficiary status revoked, effective 1/1/2022.
On 01 November 2022, the Biden Administration announced the removal of AGOA beneficiary status from Burkina Faso, effective 1/1/2023.
On 31 October 2023, the Biden Administration announced the removal of AGOA beneficiary status from Uganda, Niger, Gabon and Central African Republic, effective 1/1/2024. Mauritania was re-instated effective 1 January 2024, according to a White House announcement on 29 December 2023.
The linked table above contains the list of AGOA-beneficiaries.
AGOA’s (original) eligibility criteria - Section 104 of the Act
(a) The President is authorized to designate a sub-Saharan African country as an eligible sub-Saharan African country if the President determines that the country (see Note*) :
(1) has established, or is making continual progress toward establishing--
(A) a market-based economy that protects private property rights, incorporates an open rules-based trading system, and minimises government interference in the economy through measures such as price controls, subsidies, and government ownership of economic assets;
(B) the rule of law, political pluralism, and the right to due process, a fair trial, and equal protection under the law;
(C) the elimination of barriers to United States trade and investment, including by--
(i) the provision of national treatment and measures to create an environment conducive to domestic and foreign investment;
(ii) the protection of intellectual property; and
(iii) the resolution of bilateral trade and investment disputes;
(D) economic policies to reduce poverty, increase the availability of healthcare and educational opportunities, expand physical infrastructure, promote the development of private enterprise, and encourage the formation of capital markets through micro-credit or other programs;
(E) a system to combat corruption and bribery, such as signing and implementing the Convention on Combating Bribery of Foreign Public Officials in International Business Transactions; and
(F) protection of internationally recognized worker rights, including the right of association, the right to organise and bargain collectively, a prohibition on the use of any form of forced or compulsory labour, a minimum age for the employment of children, and acceptable conditions of work with respect to minimum wages, hours of work, and occupational safety and health;
(2) (A country that) does not engage in activities that undermine United States national security or foreign policy interests; and
(3) does not engage in gross violations of internationally recognised human rights or provide support for acts of international terrorism and cooperates in international efforts to eliminate human rights violations and terrorist activities.
(b) Ongoing Compliance:
If the President determines that an eligible Sub-Saharan African country is not making continual progress in meeting the requirements described in subsection (a)(1), the President shall terminate the designation of the country made pursuant to subsection (a).
. Note* : Proclamation 7350 delegated to the United States Trade Representative (USTR) the authority to determine whether these countries have met the two requirements described above.